Syndromes
Abernethy Syndrome
Alagille syndrome
Allgrove (triple A) syndrome
Alport's syndrome
Angelman
Ataxia-Telangiectasia
Austrian's syndrome
Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome (Gorlin syndrome)
Behcet disease
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
Biliary atresia-splenic malformation syndrome
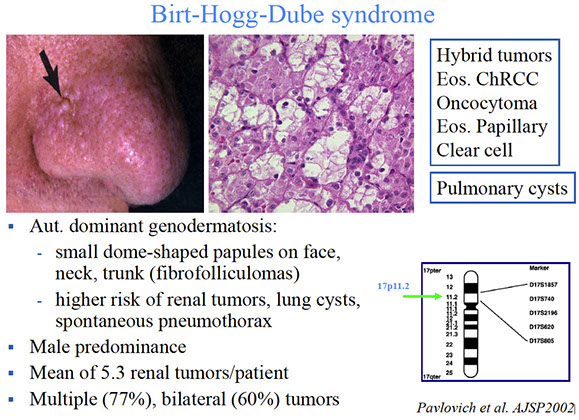
Birt-Hogg-Dube
Bloom syndrome
Blue Rubber Bleb Nevus Syndrome (BRBNS)
Brooke-Spiegler syndrome
Brugada syndrome
Caplan syndrome
Carney complex (CNC)
Carney triad
Carney-Stratakis syndrome
Cogan syndrome
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Congenital Nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type
Cowden syndrome
CREST syndrome
Cri du chat
Criggler-Najjar syndrome
Cronkhite-Canada syndrome
Dejerine-Roussy syndrome (thalamic pain syndrome)
Denys-Drash syndrome / Frasier syndrome
DiGeorge syndrome
Down syndrome
Dubin-Johnson syndrome
EBV-assoc tumors
Edward syndrome
Familial retinoblastoma
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP)
Familial Atypical Multiple Mole Melanoma Syndrome
Familial Autosomal Dominant Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
Familial Autosomal Recessive Corticosteroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome
Fanconi's anemia
Felty's syndrome
Ferguson-Smith syndrome
Gardner syndrome
Gilbert syndrome
Goldenhar syndrome
Goltz syndrome
Gorlin syndrome
Griscelli syndrome
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
Hereditary Leiomyoma and Renal Cell Carcinoma syndrome (HLRCC)
Hereditary NonPolyposis Colorectal Cancer (HNPCC; Lynch syndrome)
Hereditary Papillary Renal Cell Cancer (PRCC)
Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer syndrome
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome
HELLP syndrome
HHV-8 assoc tumors
HIV-assoc tumors
Holt-Oram syndrome (heart-hand syndrome)
Hyper-IgE syndrome
INI-negative tumors
Juvenile polyposis syndrome
Kallman syndrome
Kasabach-Merritt syndrome
Kearns-Sayre syndrome
Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome
Lennox-Gastaut syndrome
LEOPARD syndrome
Leser-Trelat syndrome
Li-Fraumeni syndrome
Long QT syndrome
Maffucci's syndrome
Mazabraud's syndrome
McCloud syndrome
McCune Albright syndrome
Meckel-Gruber syndrome
Meigs syndrome
Miller-Dieker syndrome
MonoMAC Syndrome
Muir-Torre syndrome
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasias (MEN 1,2A and 2B)
MYH-associated Polyposis (MAP)
Nail-patella syndrome
Neurofibromatosis type 1
NF2
Noonan syndrome
Ollier's syndrome
Pearson syndrome
PEComa family
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
Pierson syndrome
Pleuropulmonary blastosis familial tumor syndrome
POEMS syndrome - see Lymphoid neoplasms
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
Prader-Willi
Reed's syndrome
Retinoblastoma (Rb)
Rhabdoid Tumor Predisposition Syndrome (RTPS)
Rombo syndrome
Rotor syndrome
Ruvalcaba-Myhre-Smith syndrome
Schwachman-Diamond syndrome
Small round blue cell tumors
Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome
Smith-Magenis syndrome
Sturge-Weber disease
Stein-Leventhal syndrome
Stiff Person Syndrome (SPS)
Tuberous Sclerosis
Turcot syndrome
Turner syndrome
VATER/VACTERL syndrome
von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
WAGR syndrome
Weber-Christian disease
WHIM syndrome
Williams syndrome
Wiscott Aldrich syndrome
Wolf syndrome
Zellweger syndrome
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
***BONUS POINTS***
Tumor suppressor genes
Oncogenes
Abernethy Syndrome
Absent portal vein from birth c shunting of intestinal and splenic blood around liver to renal or hepatic veins
- micro: absent portal veins in small and medium-sized portal tracts c occasional hypoplastic portal veins in larger portal tracts
- nodular regenerative hyperplasia possibly seen
- hepatic arteries usually hypertrophied c prominent muscular coats
- mass esions can develop, such as focal nodular hyperplasia and HCC in non-cirrhotic livers
Alagille syndrome
- aka arteriohepatic dysplasia, syndromic paucity of bile ducts
AD, JAG1 mutation
- assoc c bile duct paucity, pulmonary artery stenosis, tetralogy, atrial septal defects, aortic stenosis, coarctation
- facial dysmorphism (broad forehead, widely spaced eyes, small mandible, prominent ears, imparting an overall triangular profile), butterfly vertebrae, posterior embryotoxin of the eye, and congenital heart disease (esp peripheral pulmonic stenosis)
Allgrove syndrome
aka triple A syndrome
AR; achalasia, alacrima (disorders of tear secreation), and adrenocorticotropic hormone-resistant adrenal insufficiency
Alport's syndrome
Mutation in type IV collagen leads to split BM
- assoc c nerve disorders, ocular disorders, deafness
Sx: hematuria, slowly-progressive renal failure, hearing loss
Genes: X-linked recessive, COL4A5 mutation on Xp22.3, which encodes a5 chain of type IV collagen
EM: thickening / thinning of GBM c unique "basketweave" appearance
Dx: skin or renal bx, absence of a5 chain of type IV collagen
EM: thin, disrupted and inhomogeneous lamina densa, sometimes appearing multilaminar
Angelman
Maternal 15q11.2
- hyperactivity, inappropriate laughter, aphasia, ataxia, MR, seizures
Ataxia -Telangiectasia
AR, Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated (ATM), 11q22-23
- Defective DNA repair, inc sensitivity to x-ray
Ataxia, telangiectasias in eyes and skin, thymic hypoplasia and recurrent sinopulmonary infections
- Absent IgA, ↓ IgE, ↓ CD4 T-cells
- ↑ Lymphoreticular malignancies (ALL in kiddos, solid tumors in adults)
Austrian's syndrome
Triad: endocarditis, meningitis and pneumonia; endocarditis seen in alcoholics c pneumococcal endocarditis, not seen much anymore
Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome (Gorlin syndrome)
AD, 9q22, PATCHED gene
• Numerous BCCs
• Palmar-plantar pits, odontogenic keratocysts, calcification of falx, skeletal anomalies (bifid ribs), neurologic anomalies, lipomas, fibromas, medulloblastomas, ovarian cysts
Behcet disease
Oral ulcers, genital ulcers, uveitis; pathergy test positive
- incidence highest in Middle East, Far East, and Mediterranean
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
sporadic or AD (3/20), WT2, 11p15
- Syndrome of diffuse overgrowth: high birth weight, macroglossia, organomegaly, hemihypertrophy, neonatal hypoglycemia
- Risk of embryonal tumors: Wilms tumor, hepatoblastoma, pancreatoblastoma,
Biliary atresia-splenic malformation syndrome
Polysplenia, asplenia, or double spleen
- some can have cardiovascular malformations (situs inversus, preduodenal portal vein, absent vena cava), intestinal malrotation, pancreatic anomalies
Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome
AD, 17p11.2, BHD gene (folliculin)
Kidney cancer (multifocal, bilateral, hybrid oncocytoma and chromophobe renal cell carcinoma [HOCT, nearly 10/10]), renal and pulmonary cysts / pneumothorax, and fibrofolliculomas (trichodiscomas), acrocordon
Bloom syndrome
AR, BLM helicase, cr 15
Predisposed to cancer, but esp leukemia; also other developmental defects
Blue Rubber Bleb Nevus Syndrome (BRBNS)
assoc c multiple cutaneous (congenital) and GI hemangiomas
Brooke-Spiegler syndrome
Numerous trichoepitheliomas and cylindromas
- sometimes spiradenoma or spiradenoma / cylindroma overlap syndrome
Genes: mutations in the CYLD gene on cr 16q12-q13
Brugada syndrome
Most prevalent in southeast Asia
- presents in healthy young men as sudden death during sleep
- has characteristic ECG pattern
- Mutations in 8 genes (SCN5A, GPD1L, CACNA1C, CACNB2, SCN1B, KCNE3, SCN3B, HCN4)
Caplan syndrome
Rheumatoid arthritis c intrapulmonary rheumatoid nodules and pneumoconiosis
*** put a Cap in your lungs! ***
Carney Complex (CNC)
AD, 70% familial, Protein kinase A
CNC1: PRKARIA, 17q23-24, most common, also CNC2: CNC2, 2p16.
- protein kinase regulatory subunit-alpha gene
-- has null mutations in PRKAR1A which encodes cAMP-dependent protein kinase
Clinical Manifestations:
- Skin lesions: lentigines, epithelioid blue nevi
- Myxoma: heart, skin (angiomyxoma), and breast (FA)
- Psammomatous melanotic schwannoma, upper GI schwannomas
- Breast ductal adenomas
- Testicular large cell calcifying Sertoli cell tumor
- Endocrine: primary pigmented nodule adrenocortical disease (PPNAD); pituitary adenomas (GH, prolactin), thyroid follicular adenoma
***It's complicated, even for a Carney, to TAME a LAMB***
TAME: Testicular sertoli cell tumor, Adenomas (breast, pituitary, thyroid), (atrial, skin) Myxoma, Ephelides
LAMB: Lentigines, Adrenocortical dz, Melanotic schwannoma, Blue nevi
Carney Triad
GISTs, paraganglioma, pulmonary chondroma in young women
- epithelioid, germline, mets, resistant to imatinib
Genes: SHDB IHC negative, no SDH mutations
Carney-Stratakis syndrome
Multiple gastric epithelioid GIST, paraganglioma, and pheochromocytomas assoc c germline loss of SDH (succinate dehydrogenase complex)
- resistant to imatinib
- distinct from Carney triad
Cogan Syndrome
Vasculitis with keratitis and vestibulo-auditory symptoms
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Assoc c adrenal rest tumors of the testis (10/10), which are similar to Leydig cell tumors, but are bilateral and/or multifocal, assoc c dense fibrosis and dont have Reinke crystals
Congenital Nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type
Nephrin affected on NPHS1 gene [19q13.1]
- nephrin is a key compoenent of the glomerular slit diaphragm
- affected children born with markedly enlarged placenta
- massive proteinuria begins in utero, nephrotic syndrome by 1 month of age
- EM is notable for an abnormal variation in the size of the slit pores (the space between podocyte foot processes) and rarefaction of the slit diaphragms
Cowden syndrome
- aka Multiple hamartoma syndrome
AD, PTEN/MMAC1 (a tumor suppressor), 10q23
- hamartomas involving organs from all 3 germ layers
• Hamartomatous colon polyps
• Facial trichilemmomas, storiform fibromas, mucosal lesions
- Macrocephaly
• Palmoplantar keratoses and hyperkeratotic pits
• Multiple lipomas and papillomas
• Dysplastic cerebellar gangliocytoma (Lhermitte-Duclos disease)
• Thyroid: multiple follicular adenoma or PTC
• Carcinomas of breast, thyroid, colon, endometrium, kidney
- may get immunologic abnormalities
Other PTEN syndromes: Ruvalcaba-Myhre-Smith (Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba) syndrome, Proteus syndrome
CREST syndrome
A limited form of scleroderma (systemic sclerosis)
Calcinosis; Raynaud phenomenon, Esophageal dysmotility, Sclerodactyly, Telangiectasias
Cri du chat
5p15.2 microdeletion
Abnormal cat cry, microcephaly, MR
Criggler-Najjar syndrome
Type I: Absent UDP-glucoronyl transferase (UGT1A1) causes unconjugated bilirubinemia (due to absent bilirubin conjugation), which is fatal in first few years of life
- absent conjugated bili
- negative urine bilirubin
- dec urine bilinogen
- light-brown poop
Type II (Arias syndrome) less severe (UDP-G just decreased, not absent and can be tx'd c phenobarbitol
Sx: jaundice, kernicterus, inc unconjugated bilirubin
Tx: plasmaphoresis, phototx
Cronkhite- Canada syndrome
Non-familial; high mortality c GI bleeds, prolapse and infx
Lots of gastric hyperplastic polyp-like cystically dilated lesions and more edematous (somewhat similar to juvenile polyposis) in sm / lg bowels, and may present c sx related to diarrhea
- inc risk of colorectal ca
- polyps spare the esophagus
- pts also c alopecia, onychodystrophy (from protein loss in mucoid diarrhea) and skin hyperpigmentation
BRBNS
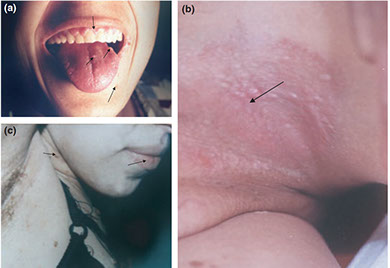
Cowden syndorme. a) Multiple oral fibromas, perioral tricholemmomas; b) papules in the pits; c) perioral tricholemmomas, oral fibromas on lower lip, verrucous papules on neck and chest and skin fibromas
Dejerine-Roussy syndrome
-aka thalamic pain syndrome
Numbness turns into chronic pain out of proportion to environmental stimulus (called allodynia or dysasthesia) after a cerebrovascular accident usually
Denys-Drash syndrome / Frasier syndrome
WT1 gene [11p13]
Not familial, WT1 point mutation (vs deletion seen in WAGR)
Wilms tumor (9/10), gonadoblastoma, male pseudohermaphroditism, diffuse mesangial sclerosis causing rapidly progressive renal failure
- renal bx shows mesangial sclerosis
- Frasier syndrome is similar but less severe, assoc c gonadoblastoma
DiGeorge syndrome
- aka velocardiofacial syndrome, Catch 22 syndrome, CHARGE sequence or Shprintzen syndrome
22q11 microdeletion, TBX1 gene. thymic aplasia / hypoplasia (immunodeficiency), parathyroid aplasia / hypoplasia (hypocalcemia and tetany), abnormal facial features, MR, 75% c cardiac abnormalities, esp conotruncal malformations (including tratralogy of Fallot, interrupted aortic arch, ventricular septal defects and truncus arteriosis)
*** CATCH 22 = Cleft palate, Abnormal facies, Thymic aplasia (T cell deficiency), Cardiac defects, Hypocalcemia from 22q11 microdeletion ***
*** CHARGE sequence = Coloboma, Heart malformation, choAnal atresia, mental Retardation, Genital hypoplasia, hEaring loss ***
Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)
Primary trisomy (95%), translocation (4%), mosaicism (1%)
50% of cases with structural cardiac anomalies, classically an endocardial cushion malformation causing a membranous ventricular septal defect
- can also get patent ductus arteriosus, atrial septal defect and AV septal defects
- can get AML M7 (acute megakaryoblastic leukemia) and transient myeloproliferative disorder (in 1/3, GATA1 genemutation), MALToma or ALL
- nearly all pts get Alzheimer-like dementia by age 40 yo
- inc risk of retinoblastoma, testicular tumors, brain tumor
- inc risk of duodenal obstruction / atresia, imperforate anus, congenital megacolon
- hypoplastic maxilla
- slanting palpebral fissures
- abundant nuchal skin
- hypotonia
- Absent Moro reflex
Dubin-Johnson syndrome
Defective canalicular multiple organic anion transporter (cMOAT)
- prob c conjugated bilirubin excretion leading to conjugated hyperbilirubinemia
Liver appears grossly black
B9
Rotor's syndrome is similar to Dubin-Johnson but is milder and does not cause a black liver
*** Get Closer, Deeper Romance ***
*** Gilbert, Cirggler-Najjar, Dubin-Johnson Rotor syndrome ***
EBV-assoc tumors
Lymphomatoid granulomatosis, nasal type extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, (Mixed cellularity) classical Hodgkin Lymphoma, plasmablastic lymphoma, AngioImmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma, Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disease (PTLD), Infectious mononucleosis (enlarged LNs), X-linked lymphoproliferative disorder, primary effusion lymphoma, oral hairy leukoplakia
- EBV+ DLBCL of the elderly, DLBCL assoc c chronic inflammation, and DLBCL NOS
- EBER (nuclear) and LMP1 (cyto / mem) ISH testing done
- can also do ISH c BamHIW sequence of EBV DNA
- EBV-ISH (+) in lymphoepithelioma-like cholangiocarcinoma
Edward syndrome
(Trisomy 18)
Babies born small and with heart defects (ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, patent ductus arteriosus), short sternum, narrow pelvis, omphalocele, esophageal atresia, microcephaly with prominent occiput, narrow palpebral fissues, ptosis, micrognathia, cleft palate, clenched fists with overlapping 2nd and 5th fingers, absent radius, webbing of second and third toes, clubfoot or rocker bottom feet, severe intellectual disability, undescended testes in males
- can also have kidney defects, choroid plexus cysts in brain
- rate of dz inc c maternal age
- occurs in 1 in 5k births; higher chance of surviving to birth if female, the chance of having a second child with the dz after having one is ~1%
Familial retinoblastoma
At risk for osteosarcoma, rhabdomyosarcomas and rhabdoid tumors
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP)
AD, Adenomatous Polyposis Coli (APC) gene, 5q
- APC usually degrades the proto-oncogene B-catenin, so when APC aint workin B-catenin builds up in the nucleus
- Colorectal carcinoma (10/10 if dont get early total colectomy) with hundreds to thousands of adenomas
- Gastric polyps: fundic gland polyps (can be dysplastic though are inert)
- Small intestine: (prox duodenal) adenomas, peri-ampullary carcinoma (MCC death after total colectomy)
- Thyroid cancer (esp cribriform-morular variant of papillary)
- Desmoids (fibromatosis), fibromas on neck, osteomas, epidermoid cysts and pilomatrixomas, unerupted and supernumerary teeth
- medulloblastomas (Turcot's)
- juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibromas
- may be "attenuated", which isnt as bad
Familial Atypical Multiple Mole Melanoma Syndrome
- FAMMM syndrome, B-K Mole Syndrome
AD, p16 mutation on CDK2NA (p21), CDK4 (21q14), CMM (1p)
>100 nevi, dysplastic / atypical nevi, inc risk of melanoma
- inc risk of pancreatic adenoca
Familial Autosomal Dominant Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
- a-actinin, ACTN4 gene; also transient receptor potential cation channel 6 by TRPC6 gene
- onset of nephrotic syndrome in adolescence or young adulthood
Familial Autosomal Recessive Corticosteroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome
- Podocin, encoded by NPHS2 gene
- onset proteinuria in early childhood
- dx: renal bx initially resembles minimal change disease but transforms into focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
Fanconi’s Anemia
AR, Ashkenazi Jews
- Chromosomal breakage syndrome, increased sensitivity to mitomycyin C, diepoxybutane
- Abnormal skin pigmentation
- Absent thumbs, microcephaly, short stature (bone hypoplasia)
- PRCA/MDS/Aplastic anemia (marrow hypoplasia)
- AML (mostly M4, M5) and other leukemias
- Carcinomas: skin, liver, stomach
- kidney and spleen hypoplasia
Renal Fanconi Syndrome
Proximal tubular dysfunction with numerous causes
- manifests as glycosuria, amino aciduria, phosphaturia, hypokalemia, and metabolic acidosis (bicarbonate wasting)
- inherited causes include cystinosis, tyrosinemia, and galactosemia (secondary tubular damage), and direct inheritance of tubular defects such as Dent disease (X linked recessive defect in the CLCN5 gene encoding a chloride channel)
Felty's syndrome
RA, splenomegaly, leukopenia c neutropenia
***FeLt your spleen, and it hurts (from the RA)***
Ferguson-Smith (multiple keratoacanthoma) syndrome
AD, MSSE gene, 9q22-31
Teen-onset ulcerative keratoacanthomas c spontaneous resoltion and recurrence
Gardner's syndrome
AD, 5q21, APC
Get FAP stuff and also assoc c osteoma (mandible of skull), odontomas, colon polyps (and colorectal ca), epidermoid cysts, congenital hyperplasia of retinal epithelium, fibromatosis of breast, supernumary teeth and lipomas, desmoid tumors, pilomatrixomas, and congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigmented epithelium (CHRPE)
*** Gardners PEDO (Spanish for fart) after eating too much*** Pilomatrixomas, Epidermoid cysts, Desmoid tumors, Osteoma, too many teeth***
Assoc c FAP (inactivation of the APC tumor suppressor gene)
- has 100% chance of colonic tubular adenomas and colon cancer
- also see dental and ocular probs, multiple skin tumors (epidermal cysts, nuchal-type and desmoplastic fibromas, lipomas, leiomyomas) and extracolonic ca's (thyroid, hepatobiliary, CNS) - caused by cilia??
Gilbert's syndrome
AR c underactive bilirubin-UGT (mutations in the 5' TATA box of the UGT1A1 promoter) causing prob c bilirubin uptake leading to unconjugated bilirubinemia
- No overt hemolysis
- Assoc c stress (fasting, viral illness)
- otherwise asymptomatic; may be present in up to 5% of whites
No tx necessary (avoid stress :) )
Goldenhar syndrome
- aka Oculo - Auriculo - Vertebral (OAV) syndrome; hemifacial microsomia
Abnormal development of first and second branchial arches
- abnormally developed ear, nose, soft palate, lip and mandible
See limbal dermoids, preauricular skin tags, and strabismus
Goltz syndrome (Basal cell nevus syndrome)
AD, PTCH
Goltz syndrome
- aka focal dermal hypoplasia
Pts have focal hair loss, abnormal nails and skeletal abnormalities
Micro: skin c slightly papillated epidermis overlying adipose tissue c no discernable dermis
Gorlin syndrome
- nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS)
AD / sporadic, mutation to PTCH gene cr 9q22.3
Sx: 2+ basal cell cas before age 20, body overgrowth, jaw keratocystic odontogenic tumor (KCOT or OKC), ovarian fibromas, congenital skeletal abnormalities, palmoplantar pits, desmoplastic medulloblastoma, other cancers (cardiac)
Griscelli Syndorme
A rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by albinism (hypopigmentation) with immunodeficiency that usually causes death by early childhood
- there are 3 different classifications of the form of disorder
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
- aka Rendu-Osler-Wber syndrome
AD, ACVRL1 (ALK1, 12q11-14) or ENG (endoglin, 9q33-34), both involved in TGF-B pathways
Aneurysmal telangiectasia in lots of organs (skin and mucosal surfaces [GI, resp, UT, and visceral organs])
- complicated by bleeding
Hereditary Leiomyoma and Renal Cell Carcinoma syndrome (HLRCC)
AD defect in Fumarate hydratase (FH), 1q42-43
PRCC type 2 c leiomyomas (cutaneous and uterine c distinct cytologic features
- can use IHC to show loss of FH
Hereditary NonPolyposis Colorectal Cancer (HNPCC)
- aka Lynch syndrome (though technically HNPCC is a more clinical diagnosis and Lynch syndrome is only confirmed after molecular dx)
AD dominant mutation of DNA mismatch repair genes, Microsatellite Instability (MSI)
DNA mismatch repair genes: MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2 and EPCAM
*** Think of them in pairs, with the lower one getting messed up first: SH's go together; MLH and PMS go together; abnormality in MLH -> PMS abnormality, MLH1 -> MLH6 abnormality ***
Lynch I = colon cancer
Lynch II: Colon > endometrial > ovary, breast
Features of colon ca:
- young pts, tubular adenoma-assoc
- rt-side of colon, large size
- poorly differentiated, often trabecular pattern
- mucinous/colloid differentiation, signet ring cells
- prominent tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL), peri-tumoral nodular lymphoid infiltrate
- medullary-like, well-circumscribed pushing margin
- LS related ovarian ca: clear cell type, younger age group (45 yo)
- 80% lifetime risk of CRC, 6/10 get endometrial, ~1/10 ovarian
- other cancers: stomach, pancreatobiliary, urothelial of upper tract (esp c inverted growth)[1/3], sm bowel, brain, skin (sebaceous adenomas, carcinomas, keratoacanthomas)
- prox colon always involved
Amsterdam criteria: 3-2-1
3 relatives (1 1st degree) c any HNPCC carcinoma; 2 generations, 1+ carcinoma in person younger than 50 yo
IHC testing can be done using MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2
- any nuclear positivity, and it is considered intact
Review algorithm NEJM 352:1851, 2005
Genes: hMLH1 is mutated in up to 3/20 sporadic colorectal ca's, so other genes should be tested to be more certain of the diagnosis of Lynch syndrome
- MSH2 can be deleted through a deletion of the 3' end of EPCAM gene which causes methylation induction of the MSH2 promoter
Hereditary Papillary Renal Cell Cancer syndrome (PRCC)
AD defect in MET (via Hepatocyte Growth Factor), 7q34
Multiple bilateral PRCCs
Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer syndrome
AD CDH1 (E-cadherin) gene mutation
Diffuse gastric ca, lobular breast ca
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome
Pts have oculocutaneous albinism (legally blind) assoc c bleeding diathesis and pulmonary fibrosis and colitis and lysosomal dysfunction
- common in Puerto Ricans
EM: Paucity of dense bodies (DB), necessary in the second phase of platelet agg
HELLP syndrome
Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes, Low Platelets
- have epigastric or upper rt quadrant pain or heartburn, malaise, nausea/vomiting
- 1/5 get DIC (disseminated intravascular coagulation), more get renal failure (??)
HHV-8 assoc tumors
Kaposi sarcoma
Multicentric Castleman's disease (and plasmablastic lymphoma
Primary effusion lymphoma
HIV-assoc tumors
Kaposi sarcoma, (B cell) lymphoma, Mycosis fungoides, Oral / anorectal SCC, Plasmablastic lymphoma, Primary effusion lymphoma,
- classical subtype of Hodgkin (usually pts also have EBV infx), esp mixed cellularity or lymphocyte-depleted, sometimes nodular sclerosis (nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma is rarely if ever assoc c HIV)
Holt-Oram syndrome (heart-hand syndrome)
AD, TBX-5 [12q]
- characteristic heart and upper limb abnormalities
- upper limb malformations may involve the radius, thumb phalanges, or carpal bones and they range from severe (phocomelia) to minimal (subtle carpal bone deformities)
- usually bilateral and symmetrical and if asymmetrical the left is more severely affected
- Cardiac malformations most commonly take the form of septal defects, especially secundum atrial septal or muscular ventricular septal defects
Hyper-IgE syndrome
Triad of eczema, recurrent skin infections, and elevated IgE levels
- pathogenesis due to skewing of TH2 differentiation, which produce increase IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13
- most common form of autosomal dominant hyper-IgE syndrome results from dominant negative mutations STAT3
- shares some features with Wiscott-Aldrich syndrome
INI-1 Negative tumors
(pediatric) ATRT
Renal medullary carcinoma
Renal rhabdoid tumor (desmin +. keratin +, INI - )
Epithelioid sarcoma
Epithelioid MPNST (1/2)
Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma (3/20)
Myoepithelial carcinoma (sometimes)
SMARCB1 (INI-1) deficient sinonasal carcinoma
Juvenile polyposis syndrome
AD, SMAD4/DPC4 (18q21), BMPR1A (10q22), and PTEN (10q23)
Juvenile polyps of stomach, small and large colon.
- Juvenile polypsois must have: JPs thoughout GI, >5 JPs in colorectum, family hx of JPs
Micro: smooth outer contour with erosion, cystically dilated mucus-filled glands, nonadenomatous epithelium, dense nonmuscular collagenous stroma permeated by inflammatory cells
Px: ↑ GI cancer, mostly colorectal adenocarcinomas, also stomach, sm intesting and pancreatobiliary
Tx: May do prophylactic colectomy.
-Note-
Juvenile polyps (in general): Sporadic, in kiddos <5 yo. 80% in rectum. Not malignant if single
Kallmann Syndrome
Affects males with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and anosmia
- most cases C linked and most of these due to mutations in the KAL1 gene on Xp22.3
- isolated growth hormone deficiency
- MC is isolated growth hormone deficiency
Kasabach-Merritt syndrome
Low platelets due to consuption by Kaposiform Hemangioendothelioma
Kearns-Sayre syndrome
very uncommon, heteroplasmic, ~4/5 from spontaneous mtDNA rearrangements/deletions, usually 4.9 kb, usually has onset before 20 yo
- very rarely can be maternally inherited
pigmentary (salt and pepper) retinopathy, external opthalmoplegia, elevated CSF protein, cerebellar ataxia, cardiac conduction block, sensorineural hearing loss, skeletal myopathy, diabetes mellitus, and hypoparathyroidism
- caused by major structural defect in mtDNA
Kasabach-Merritt syndrome
death from extensive disease and severe coagulopathy with Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma
Klinefelter syndrome
1:850 live male births
47, XXY males (4/5)
46 XY / 47 XXY mosaicism (1/10)
48 XXYY and others (1/10)
Testicular abnormalities - approx 1/10 causes of male sterility 2/2 this syndrome
- renal abnormalities
- gynecomastia
Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome
Condition affection development of blood vessels, ST, and bones
3 features:
1. Port-wine stain
2. abnormal overgrowth of ST and bone (usually in one leg)
3. venous malformations (varicose veins, inc risk of DVT)
Li- Fraumeni syndrome
aka Sarcoma, Breast, Leukemia and Adrenal gland (SBLA) syndrome; malignancies occur at an early age
AD TP53 mutations (cr 17p13.1) which normally functions to decide the fate of cells with damaged DNA (can delay cell cycle progression to repair DNA or initiate apoptosis)
- causes inc risk of sarcomas (ie osteosarcoma, adrenal ca., glial tumors of CNS, and wide variety of other tumors)
- median age of onset of ST tumors is 15 yo
Dx usually involves 3 close family members having sarcoma b4 age 45 yo
Tx in women with breast cancer and Li-Fraumeni should be mastectomy and not lumpectomy 2/2 inc risk of secondary malignancies from radiation
Lennox-Gastaut syndrome
Pediatric disorder with multiple types of seizures, MR, and abnormal EEG findings
- have worse MR with earlier onset (bwt 1-2 yo), hx of West syndrome, more frequent sx, an identifiable etiology
Dx: EEG essential
- can use imaging to look for underlying cause
Tx: variety of medical (valproic acid) and surgical (corpus callostomy) tx options
LEOPARD syndrome
AD, mutated protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 11 (PTPN11) gene (same as Noonan syndrome)
- described by Gorlin
Lentigines
Electrocardiographic conduction abnormalities
Ocular hypertelorism
Pulmonary stenosis
Abnormal genitalia
Retardation of growth
Deafness
Granular cell tumor
Leser-Trelat syndrome
sudden dermatologic onset of seborrheic keratosis (look for underlying gastric malignancy)
Long QT (LQT) Syndrome
Prolonged QT interval prediscposes to ventricular arrhythmia
- QT interval influenced by both acquired and genetic factors
- despite autosomal inheritance, 2:1 female predominance; bc has greater penetrance in females
- genetic factors now categorized by genotype (LQTS1 to LQTS7)
LQT1 (KCNQ1) - 11p15.5, encodes a portion of a voltage gated potassium channel, MC mutated gene in LQT syndrome
- exercise (esp swimming) triggered arrhythmias
LQT2 (KCNH2, HERG) - 7q35-36, encodes a second voltage activated potassium channel; 2nd MCC LQTS
- auditory stimulus or emotional stimulus triggered arrhythmia
LQT3 (SCN5A) - 3p21-25, sleep triggered arrhythmias
LQT7 (KCNJ2) - Encodes portions of a channel shared c skeletal muscle; mutations cause Andersen-Tawil syndrome (triad of episodic paralysis, long QT interval, and dysmorphic features)
-- (traditional) inherited causes: Romano-Ward syndrome (AD, no hearing loss), Jervell Lange-Nielsen syndrome (AR, with hearing loss), Andersen-Tawil syndrome
-- acquired causes: hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hypercalcemia, Medications (tricyclic antidepressants, phenothiazines, macrolide abx, class IA antiarrhthmics, class III antiarrhythmics)
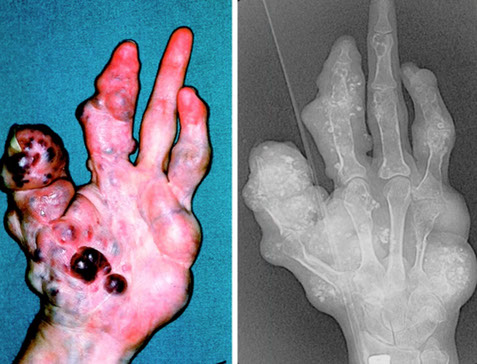
Maffucci's syndrome
Not familial, PTH1R mutations in some cases, 3p21-22
Multiple enchondromas AND soft-tissue (spindle cell) hemangiomas with a 100% malignant transformation rate (risk of developing chondrosarcoma)
- usually in small bones of hands and feet
- is deforming / disabling
Mazabraud's syndrome
Not familial, activating GNAS1 mutation, 20q13
Polyostic fibrous dysplasia and soft tissue myxomas
McCloud syndrome
Mutated Kx gene on X cr causes weak Kell antigens
- see acanthocytes on PBS
McCune Albright Syndrome
Not familial, mosaicism for mutation in GNAS1 mutation, 20q13
***the 3 P's ****
Polyostic fibrous dysplasia (multiple unilateral bone lesions)
Pigmented skin lesions (cafe-au-lait spots)
Precocious Puberty
- and multiple myxomas (ie atrial)?, thyrotoxicosis, Cushing syndrome, pituitary giganticism, breast discharge
- germline mutation incompatible with life
Caused by polyzygotic activating mutation on GNAS1 gene (cr 20)
- Gsa permanently turned on, causing crazy protein production
-- is an example of mosaicism
Meckel- Gruber syndrome
kidney dz, polydactyly, and occipital encephalocele
Meigs syndrome
Ovarian fibromas, right-sided hydrothorax, ascites (disappears after tumor excision)
Miller-Dieker syndrome
17p13 microdeletion
- Microcephaly, type 1 lissencephaly, heart malformations, renal malformations, seizures, prominent forehead, vertical furrowing of brow
Goltz syndrome (focal dermal hypoplasia)
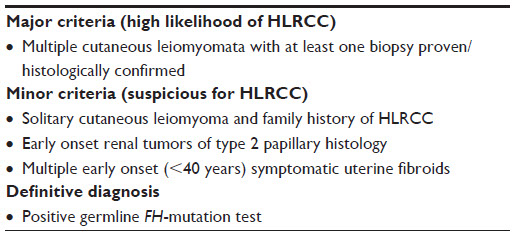
HLRCC - FH-deficient leiomyomas with little or no atypia, also c prominent staghorn vessels and chain-like arrangement of tumor cells
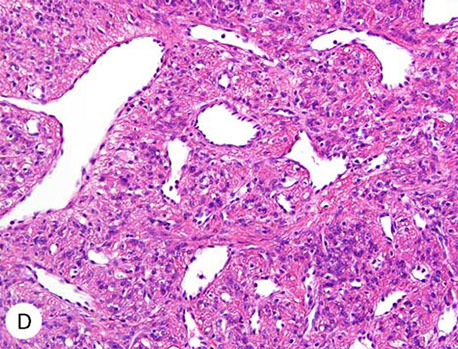
Maffucci syndrome with spindle cell hemangiomas
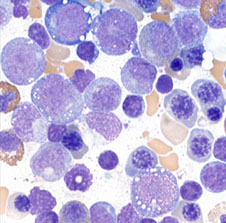
MonoMAC Syndrome
Rare autosomal dominant syndrome associated with monocytopenia, B and NK cell lymphopenia, mycobacterial viral, and bacterial opportunistic infections, and the virus infection-induced cancers
Micro: PB: anemia, monocytopenia, mild large granular lymphocytosis
- BM: patchy hypocellularity, trilineage hematopoiesis, mild dysgranulopoiesis, monocytopenia, focal caseating granuloma
Genetics: inactivating mutations in one of the two parental GATA2 genes is responsible
-12 distinct mutations in GATA2 gene have been identified
- GATA2 deficiency syndrome include AutoZone will dominant, variably penetrate MonoMAC syndrome, Emberger syndrome, familial AML/MDS, dendritic cells, monocyte, B, and NK cell deficiency
Treatment: bone marrow transplant's are currently the only treatment
Muir-Torre Syndrome
AD, HNPCC subtype c MSH2 and MLH1 mutations
hMLH1 and hMSH2 (DNA mismatch repair genes)
Sebaceous adenoma (characteristic)
Keratoacanthoma, epidermal cyst, BCC
Colon cancer, GU, endometrial, breast
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasias (MEN) 1
- aka Wermer's syndrome
AD inherited, tumor suppressor gene, 11q13 mutation, MEN1 gene, Menin protein
***3 P's: Pancreas, Pituitary, Parathyroid ***
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (ZE, insulinomas, VIPomas, glucagonomas) causing peptic ulcers, Pituitary adenoma, Parathyroid adenoma/hyperplasia, duodenal carcinoids (make gastrin, causing ZE)
- commonly presents as kidney stones and stomach ulcers
- nonendocrine lesions include facial angiofibromas, collagenomas, lipomas, and meningiomas
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasias (MEN) 2A
- aka Sipple's syndrome
AD inherited RET gene abnormality, 10q, exons 10-11
- MC > MENIIB (Gorlin)
Medullary thyroid ca (in 10/10); pheochromocytoma (in half), parathyroid adenoma (in half), cutaneous lichen amyloidosis, Hirschsprung's disease
***2P's and 1 M: Pheochromocytoma, Parathyroid, Medullary thyroid ****
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasias (MEN) 2B
- aka MEN (MEA) III, Gorlin syndrome (but is not Nevoid basal cell ca syndrome!)
AD inherited RET gene abnormality, 10q exon 16
Medullary thyroid ca (~8/10), C cell hyerplasia, pheochromocytoma (in half), diffuse mucocutaneous ganglioneuromas/neuromas (in 8/8), Marfanoid body habitus
*** 1 P, 3 M's: Pheochromocytoma, Medullary thyroid, Mucous, Marfinoid habitus ***
- Mucous = oral / intestinal neoplasias
- can also be assoc c diffuse ganglioneuromas
MYH-associated Polyposis (MAP)
AR, mostly (17/20) Y165C and G382D mutations, MYH caretaker gene is inactivated and causes APC mutations
- mostly in Europeans
Similar to FAP (up to a hundred polyps)
Nail-patella syndrome
Transcription factor that regulates transcription of COL4A3, LMX1B gene [9q34.1]
- AD, manifests c skeletal and ocular anomalies, abnormalities of the nails and renal disease (variable)
- renal bx shows BM expansion by fibrillary collagen deposits
Neurofibromatosis type I (NF1)
- aka von Recklinghausen dz
AD, NF1/neurofibromin, 17q11.2, tumor suppressor gene, down-regulating p21-ras gene
Features: multiple neurofibromas, plexiform neurofibromas, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNST; seen in 3-5%), optic nerve gliomas (pilocytic astrocytoma, bilateral), rhabdomyosarcomas, pheochromocytoma, carcinoid, cafe-au-lait spots, axillary/inguinal freckling, iris hamartomas (Lisch nodules), osseous dysplasia (spinal, and bone cysts), childhood MDS, juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia, multiple GISTS (in 7%), ampullary somatostatinoma, duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma, juvenile xanthogranuloma
- also assoc c CML and Wilm's tumor and granular cell tumor
*** CA NN OT FAI L2 B 1st *** (cannot fail to be 1st)
6 CAfe au lait spots; 2 Neurofibromas, OpTic gliomas, Freckles in Axilla and Inguinal region, Bone abnormalities, 1st degree rel.
Neurofibromatosis type II (NF2)
- aka central / acoustic neurofibromatosis
AD, NF-2, merlin/schwannomin, 22q12.2, defect in cytoskeleton
-Bilateral CN VII schwannomas
- Multiple meningiomas, spinal cord ependymomas
- Meningioangiomatosis, glioma, neurofibroma
- Juvenile subcapsular cataracts
- can have Cafe au lait spots, but no Lisch nodules
Noonan syndrome
AD, mutated protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 11 (PTPN11) gene (same as LEOPARD syndrome and some cases of Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia [JMML]); incidence in general population ~1/1,500, though the incidence in kiddos c congenital heart dz as high as 1/100
- right-sided heart defects including pulmonic stenosis and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- lymphatic malformations also common
- aka "the male version of Turner's syndrome"
- prolonged coag times (eg vWD phenotypes, factor V def, factor VIII def)
- granular cell tumor
Ollier's syndrome
Not familial, PTH1R mutations sometimes, 3p21-22
Multiple enchondromas that are mostly on the cortical surface with a 10-25% chance of malignant transformation
- comes out in early childhood presenting c finger swelling
Micro: chondromas c high cellularity and atypia in a myxoid matrix
Patau Syndrome
(trisomy 13)
Cleft lip / palate, hypertelorism (inc distance bwt eyes), proboscis (elongated nose), polydactyly, midline scalp defects, micropthalmia (small eyes), sloping forehead, flat low-set ears
Pearson syndrome
AD pancreatitis (pancreatic exocrine insufficiency) and marrow failure
- chromosomal breakage syndrome affecting the mitochondrial DNA
- marrow shows sideroblastic anemia with vacuolization of precursors
- the molecular defect is a microdeletion within the mitochondrial DNA
Vacuolization (seen with ring sideroblasts) in Peason syndrome
PEComa family
angiomyolipoma, lymphangioleiomyomatosis, pulmonary sugar tumor, clear cell myomelanocytic tumor of ligamentum teres / falciform ligament
- (+) HMB-45, MelanA, SMA, sometimes S100 (3/10)
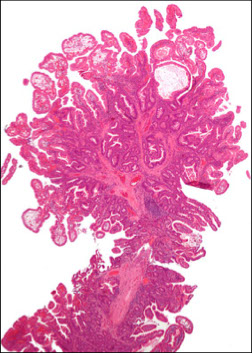
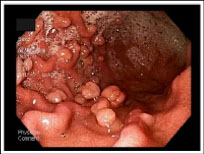
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
aka Hereditary intestinal polyposis syndrome
Autosomal dominant; STK11/LKB1, 19p13 – tumor suppressor gene, >9/10 get malignancy over lifetime
Harmartomatous polyp (mostly sm. bowel – usually jejunum)
Micro: Lined by mucinous mucosa with arborizing thin complexly branching muscle bundles
Cancers of GI tract, pancreas, breast and bladder
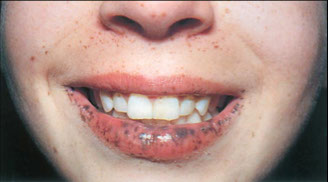
Mucocutaneous Hyperpigmentation: Dark blue or brown macules around the mouth, eyes, nose and peri-anal area
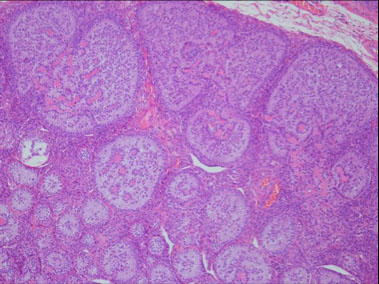
Sex cord tumor with annular tubules (SCTAT), ovary
Large cell calcifying Sertoli cell tumor, testicle
Adenoma Malignum: The neoplastic glands are lined by mucin-producing, columnar cells with basally located nuclei. The glands are variable in shape and size and surrounded by desmoplastic response
Inc risk of breast, GI, pancreas, bladder ca
Sex cord tumor with annular tubules (SCTAT), ovary
Hamartomatous polyp c sm muscle
Pleuropulmonary blastosis (PPB) familial tumor syndrome
Germline mutations in DICER1
- have PPB in the lung (solid or cystic) with ovarian stromal tumors, cystic nephroma, and thyroid lesions
- can also have chondromesenchymal hamartomas, cervical emryonal rhabdomyosarcomas, pituitary blastoma, pineoblastoma, renal sarcoma, ciliary body medulloepithelioma
Pierson syndrome
B2 laminin, encoded by LAMB2 [3p21]
- B2 laminin is a component of the glomerular basement membrane
- associated with microcoria (fixed, narrow pupils)
- death within several months
- renal biopsy shows mesangial sclerosis and crescents
POEMS syndrome
Polyneuropathy, Organomegaly, Endocrinopathy, M-protein, Skin changes (glomeruloid hemangioma)
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
see Stein-Leventhal syndrome
Prader-Willi
Paternal 15q11.2 microdeletion
- hyperphagia, obesity, hypogonadism, mild MR
Reed syndrome
AD; fumarate hydratase mutation
Multiple piloleiomyomas assoc c papillary RCC and uterine leiomyomas
Retinoblastoma (RB)
• Tumor suppressor gene, 13q14, 4/10 inherited
• Rb binds to E2F and prevents cells entering S phase
• E2F enhances transcription of c-myc and c-fos genes by binding to the promoters
• E7 protein binds to Rb protein, preventing its association with E2F
• E6 binds p53 protein, targeting it for destruction by proteasomes
- bilateral retinoblastomas, pineoblastomas, inc risk osteosarcoma
Rhabdoid Tumor Predisposition Syndrome (RTPS)
Germline inactivation of 1 allele of a gene occurs
- when mutation occurs in SMARCB1 gene, syndrome called RTPS1 and when mutation is in SMARCA4 gene is called RTPS2
- children c RTPS develop tumors at a younger age
- adults c the mutation get multiple schwannomas
Rombo syndrome
Trichoepitheliomas, milia, hypertrichosis, BCC, atrophoderma, vasodilation and cyanosis
Rotor Syndrome
AR; multiple defects in hepatocellular uptake and excretion of bilirubin pigments
Sx: asymptomatic conjugated hyperbilirubinemia, jaundice, normal lives; liver looks normal
Ruvalcaba-Myhre-Smith syndrome
- aka Bannayan-Ruvalcaba-Riley syndrome, Riley-Smith syndrome
Rare genetic condition c macrocephaly, developmental delay, multiple noncancerous tumors and tumoroid-growths like hamartomas and dark freckles on penis
- shares features c Cowden syndrome
Genes: PTEN mutations (60%)
Schwachman-Diamond syndrome
A pancreatic lipomatosis syndrome with marrow failure and exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
- the pancreas demonstrates fatty metamorphosis; pancreatic islets are preserved
- mutations in SBDS (Shwachman-Bodian-Diamond syndrome)
Small round blue cell tumors
Kiddos
Neuroblastoma (+ SYN, neg CD99)
Wilms tumor (blastema-predominant) (+ CK/ET1, desmin)
PNET/ Ewing sarcoma (+ CD99, NSE/SYN, PAS)
Medulloblastoma (+ SYN, variable GFAP)
Rhabdomyosarcoma (solid type)
Small cell osteosarcoma (variable CD99, osteocalcin +)
Lymphoblastic lymphoma (+ CD45, CD99)
Poorly differentiated synovial sarcoma
Adults
Lymphoma (+CD45, other lymphoid markers)
Small cell carcinoma (+ CK/EMA, NE markers, var TTF)
Merkel cell ca (+CK/EMA, NE markers, NF, Merkel cell polyomavir
Desmoplastic small round cell tumor (+ CK/EMA, NSE, TTF, desmin [neg actin])
Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma (+SOX-9, S100, CD99)
Small cell melanoma
Epithelioid GIST
Malignant glomus tumor
Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma
Midline NUT carcinoma
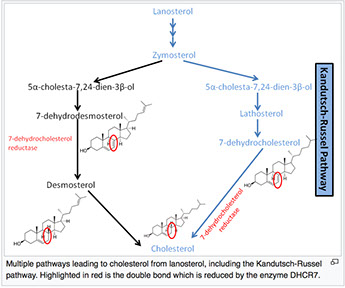
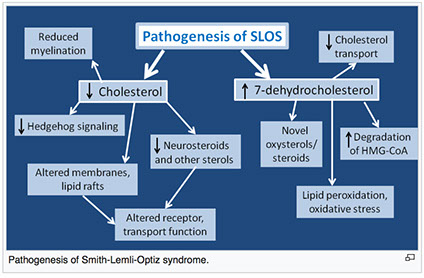
Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome (SLOS)
AR, inborn error of cholesterol synth, mutation in enzyme 7-Dehydrocholesterol reductase (DCHR7) causing hypocholesterolemia; missense mutations account for 87.6 of SLOS cases
- pts given severity score based on levels of cerebral, ocular, oral and genital defects
- MC facial features are microcephaly, bitemporal narrowing, ptosis, short and upturned nose, micrognathia, epicanthal folds, capillary hemangiomas of the nose
- can also have low-set and posteriorly rotated ears, high-arched, narrow hard palate, cleft lip, agenesis of the corpus callosum, cerebellar hypoplasia, inc ventricular size, polydactyly / syndactyly, ambiguous genitalia, congenital heart defects, renal, pulmonary and eye abnormalities
- simvastatin is an inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase and has been known to treat SLOS
Smith-Magenis syndrome
17p11.2 microdeletion
Moderate MR, prominent forehead, flat broad midface, self-multilating behavior, disturbed REM sleep
Stein-Leventhal syndrome
aka Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) or hyperandrogenic anovulation
Seen in women 18-44 yrs
Sx: anovulation, menorrhagia (heavy menstrual bleeding), hirsutism, infertility, acne, acanthosis nigricans
Due to obesity and inactivity
- can dx if: 1) anovulation, 2) hyperandrogenemia, 3) ovarian cysts
Assoc dz's: DM2, obesity, sleep anea, heart disease, mood disorders, endometrial ca,
Stiff Person Syndrome (SPS)
Autoimmune process that coexists c type I DM and other autoimmune dz's such as vitiligo, thyroiditis, and pernicious anemia
Sturge-Weber Disease
- aka Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis
No known genetic / protein defects, not inherited / familial?
• Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis
• Unilateral lesions, no familial predisposition
• Facial port wine stain/Nevus flammeus of face, especially trigeminal nerve region
• Ipsilateral leptomeningeal venous angiomas
• Calcification of superficial cortex, underlying angioma, “tram tracks”
• Hemihypertrophy of skull
• Cortical atrophy, hemiparesis, contralateral hemiatrophy of body
• Seizures, retardation
- pheochromocytomas
Tuberous Sclerosis
- aka Bourneville syndrome
AD
TSC1, 9q34, hamartin
TSC2 (MC) 16p13.3, tuberin
- TSC2 expression leads to inc mTOR activity
IHC: (+) HMB45
-Subependymal giant cell astrocytomas (SEGA)
- cardiac rhabdomyomas
- PEComas (perivascular epithelioid cell tumors): renal angiomyolipomas (2/10), clear cell "sugar" tumors, pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis (lung dz of younger women that have melanocytic and sm muscle cell markers)
-Tubers (cortical and subependymal glioneuronal hamartomas)
- rectal microhamartomatous polyps
- dermal angiofibromas (adenoma sebaceum) of face, subungual fibroma, ash-leaf patches
*** Zits, Fits, and Nit-Wits**
- zits are the angiofibromas, fits are seizures and nit-wits from low inttelligence
***TRASH SMASHAR ***
Tuberin (regulates protein translation and cell growth)
Rhabdomyomas cardiacas - nearly 100% specific for TS
Angiomyolipomas in kidney that cause flank pain (2/10)
Subependymal GC astrocytoma: "candlestick dripping" in ventricles
Hamartomas (tubers) in cortex
Seizures (infantile spasms)
Mitral regurg
Ash-leaf spots (hyperpigmented skin lesions)
Shagreen patches - rough papules c orange peel consistence c Wood's lamp
Hamartin (regulates neuronal synapse formation) and tuberin heterodimers
Adenoma sebacum - red brown papules on nose and cheeks c butterfly pattern, which are really angiofibromas
Rapamycin (sirolimus) decreases seizure freq and subepi GC size
Turcot syndrome
Type 1
- Germline mutations of hMLH1, hMSH2 or hPMS2
- Glioblastoma multiforme, colorectal carcinoma
Type 2
- Germline mutation of APC gene
- Medulloblastoma, FAP
Turner syndrome
45 XO, 1/3000 female births, neck (nuchal) webbing, wide-spaced nipples (shield chest), short stature, streak ovaries, cardiac anomalies in 1/2 of cases, bicuspid aortic valve is MC defect, then coarctation of the aorta. Aortic root dilation is common and may lead to aortic dissection
- single umbilical artery
assoc c ganglioneuromas and gonadoblastomas
VATER / VACTERL Syndrome
Vertebral anomalies, Anal atresia, Tracheal-Esophageal fistula, Renal and Radial defects (VATER), also known as Vertebral anomalies, Anal atresia, Cardiac defects, Tracheal-Esophageal fistula, Esophageal atresia, Renal and Radial defects, Limb defects (VACTERL) syndrome
- caused by undefined defects in development of embryonic mesoderm
- unknown etiology, probably multifactorial
- liver can show absent/atrophic portal veins c inc prominent arterioles in portal tracts
- liver findings similar to Abernethy syndrome (focal nodular hyperplasia)
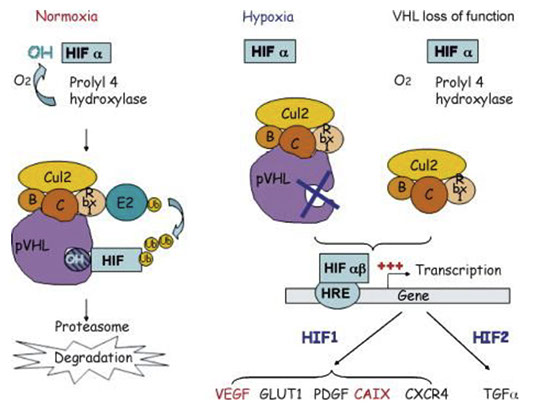
von Hippel-Lindau
AD familial ca syndrome
vHL tumor gene suppressed on 3p25-26, involved in ubiquination
CNS hemangioblastoma (Lindau's tumor in cerebellum) / cavernous hemangioma, retinal angiomas, renal cysts, RCC (clear cell type), pancreatic cysts, pancreatic serous cystadenoma, islet cell tumors, epididymal/ovarian papillary cystadenoma(1/3 of males, can be Pax2+), endolymphatic sac tumor in ear (Heffner tumor), Adnexal Papillary Cystadenoma of Probable Mesonephric Origin (APMO, 8/8), Epididymal cystadenomas
WAGR syndrome
Germline 11p13 deletion (not familial), involving PAX6 gene (aniridia) + WT1 gene
- Wilms tumor, Aniridia, Genitourinary anomalies, Retardation (mental)
Weber-Christian disease
aka Idiopathic relapsing febrile non-suppurative panniculitis
Rare dz of middle-aged females c recurring inflammation of fat what can form subq nodules which heal c depression on overlying skin
- form of panniculitis
WHIM Syndrome
Warts, hypogammaglobulinemia, infx. myelokathexis (retention of neutrophils in BM stroma) -- neuts only
- associated with CXCR4 mutations (seen in LPL)
William syndrome
elastin gene, 7q11.23 microdeletion
- dysmorphic (elf-like) facial features, abnormal dentition, MR, short stature, hypercalcemia, abnormalities of CT (hernias, diverticula, joint laxity, skin laxity) and structural cardiac and vascular defects
- most distictive cardiac anomaly is supravalvar aortic stenosis (hourglass stenosis)
Wiscott Aldrich syndrome
X-linked, WASP gene defect
- Thrombocytopenia, infection, eczema
- Small granulated PLT, no δ granules EM
- ↑ IgE and IgA, ↓ IgM and IgG
- T cells present but ↓ response to mitogens
- ↑ Malignancy
Wolf syndrome
4p deletion
- IUGR, heart malformation, microcephaly, cleft lip and palate, broad nasal root, severe MR
Zellweger Syndrome
One of a group of 4 related dz's called peroxisome biogenesis disorders (PBD), caused by defects in 1 of 13 PEX genes needed for normal function of PEX genes
- needed for normal brain development and help form myelin
- have hepatomegaly, high forehead, underdeveloped eyebrow ridges, wide-set eyes, neurologic abnormalities (seizures), lack muscle tone
- px is poor
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Gastroma causes hypergastrinemia leading to inc acid secretions and severe Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
Gross: very hypertrophied rugae in body and fundus, atrophic antrum
Micro: inc parietal cells, dec foveolar
Tumor Suppressor Genes
• RB 13q14
• P53 17p13
• APC 5q21
• VHL 3p25
• NF-1 17q11
• NF-2 22q12
• P16 9p21
• WT1 11p13
• PTEN 10q23
• BRCA1 17q21
• BRCA2 13q12
• ATM 11q22
• DCC 18q21
Oncogenes
• HER2/Neu
• c-Kit
• PDGFRA
• RAS
• ABL
• ERB-B (EGFR)
• MYC (C, N, L)
• RET
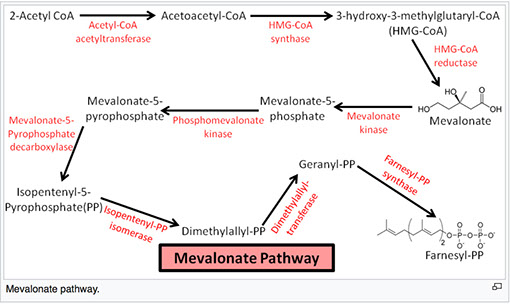
Farnesyl PP eventually converts to lanosterol
Degradation of hypoxia induced factor 1 α (HIF α)
References
1. Amer, M et al. Cowden's syndrome: a clinical, immunological and histopathological study. Int J Derm 2011, 50, 516-521
2. Fumarase-deficient Uterine Leiomyomas: An Immunohistochemical, Molecular genetic, and Clinicopathologic Study of 86 Cases. Miettinen M et al. Am J Surg Pathol 2016; 40:1661-1669
