Mycobacterium
Mycobacteriaceae
- Tuberculosis
- Bovis
- Leprae
Mycobacteriaceae
M tuberculosis complex: M tuberculosis, bovis, bovis BCG, canettii, caprae, microti, pinnipedii and africanum
Slender, straight or slightly curved rods
- Acid Fast considered Gram positive but c unique cell wall (has N-glycolylmuramic acid and not N-acetylmuramic acid)
- No spores, No capsule
- Unique cell wall: lipids, fatty acids, waxes, Mycolic Acid, hydrophobic
- Resistant to physical and chemical agents
- Resistant to drying, hydrophobic
- for safety should have a Biologic Safety Cabinet (BSC) that draws 75-100 linear feet of air per minute to ensure that HEPA filter not clogged
- can discontinue airborn isolation if 3 sputums and a AFB smear negative Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT) are negative
- Mycobacteria form circumferential rings when infx is in the ileum bc that is the direction of the lymphatics, whereas typhoid fever is longitudinal bc that is the direction of the Peyers patches
Dx: gold standard is culture c both solid and liquid media
- solid cultre can be modified LJ tubes and agar-based 7H10 or 7H11
- NAAT and fluorochrome stain best to detect org directly from specimen (but should be cultured too)
NAAT detects M tuberculosis directly by amplifying spec nucleic acid sequences using a nucleic acid probe combining direct smear rapidity c sens and spec of culture
- NAAT done c culture on first sputum (CDC rec)
- if AFB stain + and NaAAT neg = non-TB mycobacterial infx
- if NAAT + and AFB neg = dx pulmonary TB
- Latent TB detected c PPD (Purified Protein Derivative; supernatant precipitate of TB culture c lots of ag's [which other non-TB myobacteria have, which causes + result in ppl c BCG or prev non-TB mycobacteria infx])
- DNA probe assay used to id M tuberculosis complex, MAC, M kansasii and M goronae from pos acid fast cultures
- also used to speciate are DNA probes / sequencing, line probes or HPLC
- low power scans of fluorochrome-stained smears used to screen for AFB
- Interferon-Gamma Release Assays (IGRA) detect Inf-gamma release from lymphs in TB infx (no false +) which are either EIA (QuantiFERON TB) or an enzyme-linked immunospot test (T-SPOT)
- IS6110 Restriction Length Polymprphism (RFLP) analysis is the best molecular way to determine strain relatedness
- Mycobacterial intersepersed repetitive units variable number tandem repeat (MIRU-VNTR) is being increasingly used as first-line fingerprinting method that may replace IS6110 RFLP
Acid Fast Stains
Ziehl-Neelson Stain (hot stain procedure)
- Classic Acid Fast stain
- Carbol fuchsin +heat, Acid-alcohol decolorizer
- Methylene Blue counterstain
- AF organisms appear as red bacilli against a blue background
Kinyoun's Stain (cold stain procedure)
- Cold AF stain (no heating required)
- Increased conc. of basic fuchsin + phenol
- Malachite Green used as counterstain
Fluorochrome Method (Truant's Auramine-Rhodamine)
- Fluorochrome dyes complex to mycolic acids in cell wall
- Potassium permanganate used to quench non-specific fluorescence
- AF organisms appear as fluorescent bacilli against a dark background
- More sensitive, recommended for initial screening of smears
- Can scan smear at 250X
- Fluorochrome smears can be restained using classical procedure
Digestion-decontamination methods
N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine-NaOH (NALC-NaOH)
- Most commonly used method
- NaOH is for decontamination
- NALC is a mucolytic agent
4% NaOH
- Phenyl red indicator
- Used for heavily contaminated specimens
Benzalkonium Chloride (Zepharin)
- Trisodium phosphate method for digestion & decontamination
Media for Culturing Acid-Fast Organisms
Lowenstein-Jensen Medium
- Whole eggs, potato flour, glycerol, malachite green (an inhibitor which gives the media its color), No agar; takes up to a month
- Asparagine stimulates Niacin production
- Lowenstein-Jensen Gruft: same as above with added Penicillin, Nalidixic Acid, and RNA
Middlebrook 7H10 agar
- Clear medium, agar based
- Biotin, pyridoxine, malachite green, OADC enrichment (oleic acid, bovine albumin, fraction V, glucose, catalase)
Other Culture Media
Broth media are required by the CAP, and are the gold standard, are permutations of the Middlebrook agar
- Middlebrook 7H11 selective agar
- Middlebrook 7H9 broth for surgical specimens & normally sterile fluids
- BBL MGIT (Mycobacteria Growth Indicator Tube)
- MGIT tubes are read daily for an orange-red fluorescence
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
NAP +, cording+, Niacin+, forms bird nest colony on Middlebrook 7H10, catalase neg, Reff buff colonies
- Cord factor may be viulence factor causes cord-like araangement of orgs in broth - good for identification in 3rd world countries, should have 75% sensitivity
- Person to person (P2P) spread via droplet nuclei
- Inhalation of a single viable organism can lead to infection, kills ~ 2 mil/yr; 1/3 humans infected
Primary TB - nonimmune host (usually kids) that forms Ghon complex (caseating granulomas in hilar nodes and Ghon focus in lower lobes) which can heal (9/10), cause progressive lung dz (in immunocomp), severe bacteremia (miliary TB, leads to death), or become dormant and later evolve in extrapulmonary sites or cause secondary TB - most cases asx and become latent, bad infx (miliary or lung dz) c poor immune status (kids, AIDS)
Secondary TB in 1/10 healthy ppl and more c immun compromised have TB reactivated (relapsed), fibrocaseous lesions in lung and other organs (renal)
-Multi-drug resistent TB resistant to at least isoniazid and rifampin, is extensively drug-resistant if also resistant to fluoroquinolones and a second-line injectable drug
Sx: Dz only in lungs in most patients with granuloma formation, caseous necrosis, and cavitary disease
- Systemic disease sometimes develops, affecting kidneys, spleen, bone marrow, CNS, intestinal tract
- Tubercule: characteristic lesion of TB
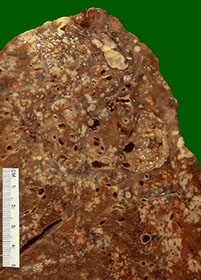
- Caseation: form of necrosis where tissue forms a dry amorphous mass resembling cheese.
- Miliary lesions: small whitish nodules on skin, (resemble millet seeds)
- Cord Factor: a cell surface glycolipid acts as a virulence factor, allows intracellular survival of organisms
- Cord Factor activity requires oxygen, thus predilection for lung tissue
- immunocompromised pts c CD4+ counts <200 usually do not have cavitary lesions on CXR bc do not have cell-mediated immunity
DX: dependent on isolation & identification
- PPD > 5mm is positive in immunocomp pts
Specimen: MC specimens are pulmonary secretions, including sputum, lung biopsy, induced sputum, bronchial wash and also gastric lavage, CSF & other body fluids (urine)
Dx: Acid Fast (beaded, slightly curved) and NAAT
- Slow growing (2-4 wks.)
- Colonies are rough, dry, friable, wrinkled, heaped
- No true pigment, (described as buff colored)
- Niacin, nitrate and pyrazinamidase Positive
- Growth at 37 C, NG at 45 C or room temperature
- Growth is said to be Eugonic (good growth)
- urea positive, <45mm foam catalase, 68 F catalase negative, Resistant to TCH
- tuberculin skin test poor sens/spec in active dz
Tx: give at least 6 months of InSPIRE tx for active dz
Mycobacterium bovis
Slow-growing nonchromogenic bug that grows in standard mycobacterial culture @ 37C
- Can cause pulmonary or extrapulmonary disease
- Formerly acquired from raw (unpasteurized) milk, thus assoc c abdominal dz (17% of Mexi cows pos)
- Part of the MTB complex
- Niacin negative, nitrate negative, pyrazinimidase neg, colonies are smooth and thin, 68F catalase neg, TCH susceptible
- Growth is said to be dysgonic (poor growth)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex
- includes: M. tuberculosis, M. bovis, M. bovis BCG, M canettii and M. africanum
Mycobacterium africanum
Rough colony, gefative 68F catalase, variable niacin, negative nitrate, pos pyrazinamidase, variable TCH susceptibility
Mycobacterium canettii
Smooth LJ colony, pos niacin/nitrate/pyrazinamidase, TCH resistant
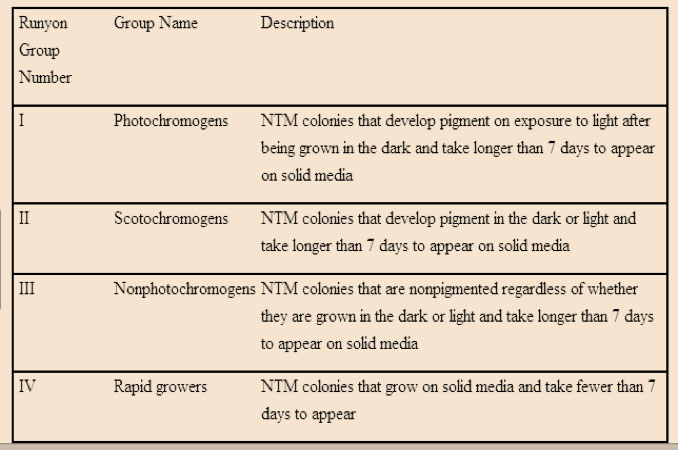
Nontuberculous Mycobacteria (NTM)
- Also referred to as MOTT (Mycobacterium other than Tubercule bacilli)
- Runyon's Classification based on growth rate and pigment production, based on how fast it grows (more or less than 7 days, slow vs rapid growers) and whether or not it produces pigment when exposed to light
- the slow growers are grouped into groups 1-3 and the group 4 is the rapid growers
- can be id'd to spp by phenotypic characteristics, DNA probes, NAA, or gene sequencing
- should do microbroth dilution for susceptibility test
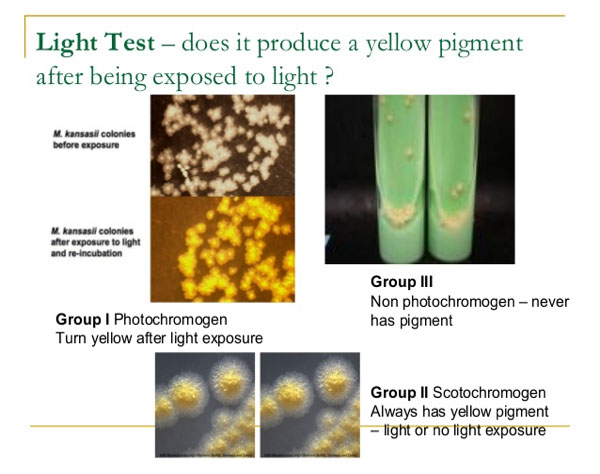
Photochromogens (Grp 1)
Pigment produced only after exposure to light; slow
- consist of M simiae, marinum, asiaticum, kansasii
*** SMAK the photographer ***
m Simiae - weakly photochromogenic, rarely cause dz
m. Marinum - rapid growing photochromogen that grows in standard mycobacterial culture media @ 30C
- assoc c freshwater fish, swimming pool granuloma (aquarium granuloma) and other cutaneous infx c secondary lymphadenitis like sporotrichosis
m. Asiaticum - pulmonary disease (Australia)
m. Kansasii - chronic pulmonary infections that mimic classic TB, commonly in white males c underlying pneumoconiosis, shepherd crook
- reservoir is H20, not spread P2P
- 2nd MCC of NTM (after MAC)
- classified using hsp65 or proB
- tx is isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol
Scotochromogens (Grp 2)
Always pigmented, Yellow pigment produced even without exposure to light; slow growing (>7 days), consist of M flavescens, gordonae, thermoresistable, scrofulacum
*** see FinGorTSS in the dark !!! ***
m. Flavescens - saprophyte
m Interjectum - chronic lymphadenitis, pulm dz
M. gordonae - tapwater bacillus. water, soil. (saprophytic); non-pathogenic
m Thermoresistable -
M. scrofulaceum - 2nd MCC cervical adenitis (scrofula) in children (after MAC)
- negative for nirate and niacin; 68C catalase pos
- see cseating granulomata and matted LNs
- tx: surgery, calrithromycin and ethambutol or rifampin
M. szulgai - pathogen, pulmonary disease predominantly in middle- aged men, cervical adenitis, bursitis, scotochromagen at 35-37C, photo at 25C
Nonphotochromogens (Grp 3)
No pigment produced, not affected by exposure to light; slow
*** HUGE MAX ***
*** Haemophilum, Ulcerans, GEnavense, M Avium-complex, Xenopi ***
m. Avium-complex (MAC)
Slow-growing nonchromogen
- Includes M. avium and M. intracellulare
-- M avium is non-pigmented, MCC non-TB lung dz
- MC as disseminate dz in pts c AIDS and CD4+<50, gets into reticuloendothelial system
- 2nd MC isolated AFB other than TB in U.S. and A
- Can cause serious TB-like disease very difficult to treat
- Common in AIDS patients - numerous organisms in blood & stool
- MCC cervical adenitis in kiddos (scrofula)`
- can get pneumonitis-like syndrome if exposed in reacreational hot tub (resistant to chlorination)
- micro shows foamy macrophages, like Whipple dz, does not always have caseating granulomas
m. Xenopi - pigmented, grows best @ 40-45C, arylsulfatase pos
- can form biofilms on pipes
- saprophyte, occasionally chronic pulmonary & extrapulmonary disease
- cause cavitary lesions in upper lobe
- detected c molecular 16S rRNA , hsp65 or rpoB
- tx is macrolide, rifampin, and ethambutol c moxi
m. Haemophilum - nonchromogenic slow-growing pathogen that requires Fe (Hemin)- or Ferric ammonium citrate supplemented media and incubation @ 30C, doesn't grown on standard media at 37C
-disseminated disease in immunosuppressed, 2nd MCC of cervical lymphadenitis in kiddos (after M avium), skin lesions in immunosuppressed
m. Ulcerans - ulcerative cutaneous or subcutaneous lesions; causes Buruli ulcer
m. Genavense - disseminated disease in AIDS patients (wasting disease)
Others!!! (M malmonense, heidelbergense, shimoidei)
Rapid Growers (Grp 4)
- Mature colonies develop in 3-5 days at 35C or in 5-7 days at 25 C, cause wide spectrum of dz, form biofilm
- Many saprophytic species in this group, common in tap water
*** Grp 4 grows FACh (fast) ***
*** Fortuitum, Abscessus, Chelonae ***
M abscessus subsp Abscessus - rapid grower that causes skin and soft tissue infx or postop wound infx; disseminated dz in immunocomp pts
- smooth or rough colonies, no Fe uptale but is NaCl tolerant, neg citrate/nitrate and mannitol
- is very resistant to meds, be scared!!!
***can live in the salty skin conditions but doesn't stand the blood's iron ***
M. fortuitum - abcesses or pulmonary disease
- rough colonies, (+) rust Fe uptake, pos NaCl tolerance, doesnt use citrate as substrate, pos nitrate and mannitol
***it is strong (Fortuitum) in that it can live in both the skin and blood (pos Fe uptake and NaCl tolerance)
M. chelonae - abcesses or pulmonary disease
- Fe neg, uses citrate as substrate, cant grow in 5% NaCl, rough colonies, neg mannitol
*** the chela is too chill to care about either the blood or skin (Fe uptake and NaCl neg)***
M mucogenicum - assoc c wound injuries after trauma and sepsis in catheter
- smooth colonies, tan Fe uptake, NaCl intolerant, citrate+ but neg nitrate and mannitol
M. fortuitum, M. chelonae, and M. abcessus 90% of clinical dz in rapid growers
Saprophytes
Dont fit well into the above groups; low virulence
M. phlei - found in grass and water
M. smegmatis - human genitalia
Immunity
- Humoral antibodies are present but do not correlate well with resistance.
- Resistance is determined by Cell Mediated Immunity (CMI)
Tuberculin Test
- Intracutaneous injection of Purified Protein Derivative (PPD-S)
- Observe for induration 48-72hrs. post injection >10mm
- Tuberculin test positive in 4-6 weeks after infection
Vaccination
- BCG is used in some countries (Bacillus of Calmette & Guerin)
- Injection of live attenuated avirulent M. bovis
- Tuberculin test positive c BCG vaccine
Tx
- If skin test positive, treat with INH for one year
- Use two or more primary drugs to prevent resistance
- InSPyRE treatment given for 6 months in active dz
Primary Drugs
- Isonazid (INH), Rifampin, Streptomycin, Ethambutol
Secondary Drugs
- Pyrazinamide, Capreomycin, Cycloserine, Ethionamide, Kanamycin, Viomycin, Paraminosalicyclic acid (PAS)
*** InSPyRE: Isoniazid, Streptomycin, Pyrazinamide, Rifampin, Ethambutol ***
Multidrug-Resistant TB (MDR TB) - resistant to INH and Rifampin
Extensively Drug-Resistant TB (XDR TB) - rare type of MDR TB that's also resistant to fluoroquinolones and other second degree drugs
Mycobacterium leprae
- Not normally be cultured on artificial media
- PCR can detect & identify M. leprae in infected tissue
- Organisms are found singly, in parallel bundles, or in globular masses in scrapings from skin and mucous membranes (likes cold places)
- Appear as typical AFB using the Acid Fast stains
- AFB often found within endothelial cells of blood vessels or mononuclear cells
- Human strains inoculated into foot pads of mice produce granulomatous lesions
- Inoculated Armadillos develop extensive lepromatous leprosy
- Man is the only known natural host, though is found in 7-banded armadillo in souther USA
Leprosy (Hansen's Disease)
Dz of the upper resp tract, skin and peripheral nerves
- 3rd MCC blindness worldwide
- Most infected individuals are asymptomatic
- transmitted when kids exposed for prolonged periods, in Texas, Hawaii, and Louisiana (armadillos)
- Nasal secretions from infected individuals
- About 10% of children so exposed may acquire disease
- Currently more than 10 million cases worldwide (Mostly in Asia)
- Lepromatin skin test can be used to differentiate leprosy types (positive in tuberculoid and borderline tuberculoid disease
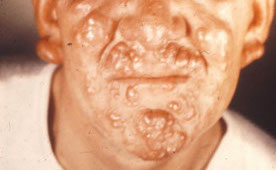
Lepromatous Leprosy
- Anergic disseminated form, can be transmitted
- Course is progressive and malign with nodular skin lesions, can be lethal
- Slow symmetric nerve involvement
- Numerous AFB in hypoesthetic skin lesions in cooler body spots, continuous bacteremia
- cell mediated immunity is deficient & skin is infiltrated with suppressor T cells
Micro: Foamy histiocytes (little-cell immunity)
*** Massive numbers of organisms on Fite stain (clumps and globules)
Labs: negative lepromin test
Tx: pts require life-long tx,
- 4,4-diaminodiphenylsulfone (Dapsone)
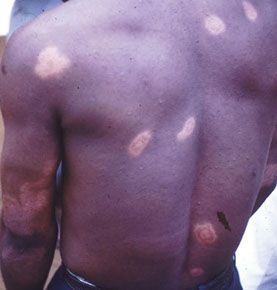
Tuberculoid Leprosy
- Localized form
- Course is benign and nonprogressive
- Macular skin lesions develop with peripheral nerve thickening with numbness
- Lepromatin skin test is positive
- CMI intact and skin infiltrated with helper T cells
Micro: epithelioid cells, giant cells, non-caseating granulomas, lymphocytes
*** Few organisms on Fite stain*** (paucibacillary)
Labs: positive lepromin test
Tx: treatment stopped with healing of lesions
- also 4,4-diaminodiphenylsulfone (Dapsone)
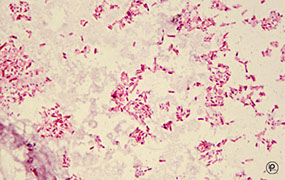
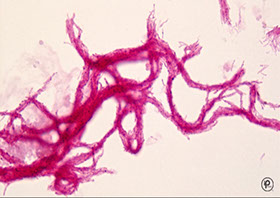
Chording on a Ziehl-Neelson
Acid fast
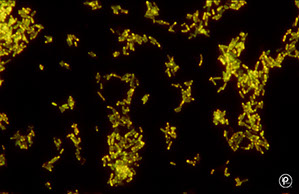
Auramine-Rhodamine
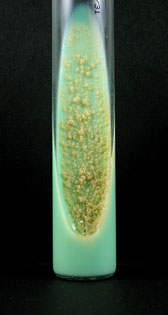
TB on an LJ slant
Positive colonies on Middlebrook 7H11
Caseous necrosis of lungs
Runyon's Classification
Lepromatous leprosy
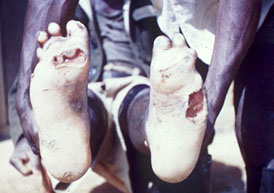
Polyneuritic trophic ulcers
Lepromatous leprosy - peripheral involvement

Tuberculoid leprosy
References
1. CLS notes
2. Osler notes
