CSF Cytology
Benign CSF
Adenocarcinoma
Astrocytoma
Plasma Cells
Cryptococcus neoformans
Benign CSF
Sample should be prepared immediately or can be refrigerated at 4C (should NOT be frozen)
- if preparation won't occur for >48 hrs, should add equal vol c 50% ethanol to preserve specimen
Should be nearly acellular, except for a small amt of lymphs and neutros, sometimes a few histiocytes and b9 lining cells are seen
- an inflam response has elevated neutros and lymphs
- blood can also be seen in a traumatic tap
- blood vessels, muscle, adipose, and fibrous tissue are considered contaminants
Plasma cells are an abnormal finding (see below)
Neutrophils assoc c acute bacterial meningitis, CMV radiculopathy, toxoplasma meningoencephalitis, and peripheral blood contamination
Eosinophils can be seen with coccidioides immitis infx
Subarachnoid hemorrhage can cause an increase in hemosiderin-laden macrophages
- may also see Germinal Matrix Cells, which can look like blasts or small blue cell tumors in the CSF
Benign germinal matrix cells in the CSF of a neonate [1]

Malignancy CSF
A fluid positive for malignancy usually is indicative of invasion of the leptomeninges or ventricular ependymal membrane
- primary tumors include meningioma, glioblastoma, ependymoma, choroid plexus papilloma, medullomastoma, sarcoma, and pineoloma
--- may see acute leukemia / lymphoma in CSF
Metastatic tumors usually from lung, breast, renal, GI, or melanoma
- usually produce diffuse meningeal carcinomatosis c abundant malignant and inflam cells
- background usually c protein deposits, blood and cellular debris
Adenocarcinoma in CSF
Most common types of metastatic adenoca to CSF:
Lung, Breast and Gastric
Cells often present singly or in small clusters
Nuclei are irregular, 3-D and eccentrically located
Nucleoli are often present
Cytoplasmic vacuolization may be present

Astrocytoma
Cells in small clusters c irregular nuclear atypia, high NC and coarse to hyperchromatic chromatin

Astrocytoma
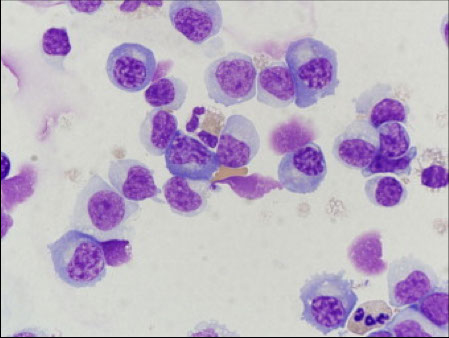
Medulloblastoma
Can be confused with adenocarcinoma, usually in pediatric pts, can also look a little like small cell ca 2/2 nuclear molding
Medulloblastoma

Mollaret Meningitis
Rare form of aseptic meningitis c recurring attacks of fever, headache, and neck stiffness
- sx appear suddenly, last for 5-7 days and then resolve spontaneously but then recur again after several days to years
Some have been found to be caused by HSV 1 or 2
- reactivation of latent HSV explains the periodic and self-limited nature of the illness
Dx made clinically after excluding other causes of aseptic meningitis
Micro: cytologic findings are non-specific, but usually has marked predominance of monocytes
- Mollaret cells: monocytes c deep nuclear clefts that leave a footprint-like appearance in the nucleus, and are seen in the first 24 hours after sx onset
Mollaret cells

CSF Plasma cells???
Associated with: Multiple Sclerosis
Also associated with:
Viral meningitis
Lyme disease
TB
Cysticercosis
Syphilis

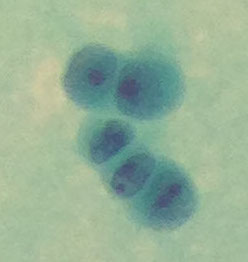
Cryptococcus neoformans
MCC CSF fungal infx
References:
1) Li W. Germinal matrix cells: mimicker of blasts or small blue cell tumors in cerebrospinal fluid. Cancer Arch 2019
